iServer configuration file introduction |
Feedback |
The main configuration information for SuperMap iServer
is located in WEB-INF ( 【SuperMap iServer Installation directory】\webapps\iserver\WEB-INF).
For the directory description, please refer to: Directory
description after installation .
Introduction to config file
The WEB-INF folder stores the configuration information
of the server and the services it provides. The folder structure is as
follows:
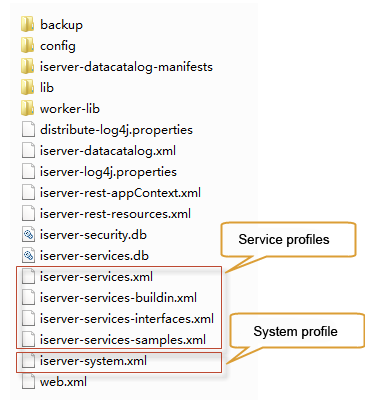
Among
- The backup folder stores the backup of the
server configuration information. See the backup
server configuration for details.
- Config folder: config file, including caching
schemes for Bing Maps, Tianditu Maps, cloud services, etc.
- iserver-datacatalog-manifests: configuration
information storing data under data catalog services.
- The lib folder stores the jar files on which
the SuperMap iServer runs.
- Worker-lib: Holds the servlet-API.jar needed
to start a multiprocess Worker node.
The main contents of each config file are shown in
the following table:
Contents of config file
| File name |
Description |
| iserver-datacatalog.xml |
The data catalog services config file contains the configuration
of the data store in the data catalog services and some other
configuration information. |
| iserver-log4j.properties |
The config file of the log. |
| iserver-rest-appContext.xml |
REST applies a config file, which defines the mapping of representation
types to URI suffixes. |
| iserver-rest-resources.xml |
The resource config file of the extension resource, where the
user can specify the name, URI, type, expression generator name,
parameter resolver name, and so on of the extension resource. |
| iserver-services-interfaces.xml |
The service interfaces instance, which contains the iserver-services-samples.xml
and the iserver-services-user.xml. Interface instances used in,
such as rest, restjsr, wms111, wms130, wfs100, wmts100, wmts-china,
wcs111, wcs112, handler, gpserver. |
| iserver-services-samples.xml |
The configuration information of the sample service provided
by the product. |
| iserver-services.xml |
The configuration information of the service published by the
user. The server recognizes this file as a service config file
as long as it starts with "iserver-services", and supports
multiple user-defined service config files, such as iserver-services-1.xml,iserver-services-2.xml. |
| iserver-services-buildin.xml |
Configuration information of iServer built-in services (such
as Geometry service and map service). |
| iserver-system.xml |
SuperMap iServer system-level configuration, including meta
information, cluster, kml style configuration, etc. |
| web.xml |
The initialization config file of SuperMap iServer defines
the mapping relationship between functions and classes. |
| iserver-security.db |
A database for storing information about users, roles, and
so on. |
| iserver-services.db |
The database where the user stores service authorization information. |
Service config file
SuperMap iServer services are composed of service providers,
service components, and service interfaces. The configuration information
for all services is stored in the service config file. It is mainly used
to provide the service interfaces config file of interface instances (iserver-services-interfaces.xml),
the config file for the sample service (iserver-services-samples.xml)
and the config file for the user publish services (iserver-services.xml).
The latter two are similar in structure and will not be described here.
With the service config file, you can:
service interfacesconfig file
Service interfaces config file iserver-services-interfaces.xml,
including service interfaces instance, root node is < application >
element, including < interfaces > child node elements, where each
interface element is used to configure a specific service interface, including
the following attributes:
- The name attribute, the name of the service
interfaces.
- The class attribute, the implementation class
of service interfaces.
- The config element, configuration information
for service interfaces.
Demonstrate service instanceconfig file.
Demonstration service instance config file iserver-services-samples.xml,
including the configuration information of the demonstration service instance
provided by the product. The root node is the < application > element,
including the following child node elements:
1. <components>
Each of these component elements is used to configure
a specific service component.
- The name attribute, the name of the service
components.
- The alias attribute, the alias of service components,
can be set to Chinese.
- The class attribute, the implementation class
of the service components.
- The interfaceNames attribute, the service interfaces
bound to the service components.
- The providers attribute, service providers
by service components.
- Config element, configuration information of
service components. It contains class, outputPath, outputSite, workspace
Path, and so on. For details, see the configure
service components through XML file. When the outputPath and outputSite
properties are not included, the system takes the corresponding values
in the < properties > element. The data component also contains
the editable attribute, which sets whether the data component is editable.
Editable when editable is true.
Note: In addition to the above attributes, the component element of the
user published service configuration file (iserver-services. xml) also
supports the initPriority attribute, which represents the priority of
GIS service startup. The higher the priority value, the higher the GIS
service startup order when starting iServer.
2. <providers>
Each of these provider elements is used to configure
a specific service provider.
- Name attribute, service provider.
- The class attribute, the implementation class
of the service providers.
- The inner-providerNames element is used to
set the service providers clustered by the cluster service providers
when cluster service providers or aggregate service providers are
used. And service providers aggregated by aggregated service providers.
- The config element, the configuration information
of the service providers, includes the setting of the workspace. It
contains class, outputPath, outputSite, And so on. For details, see
the configure
service providers through XML file . When the outputPath and outputSite
properties are not included, the system takes the corresponding values
in the < properties > element.
3. <componentSets>
Each componentSet element is used to configure a component
set, and each component set can reference multiple service components.
4. <providerSets>
Each providerSet element is used to configure a provider
set, and each provider set can reference multiple service providers.
Built-in service config file
Built-in service config file iserver-services-buildin.xml,
including configuration information of geometry service provided by iServer,
root node is the < application > element, including the following
child node elements:
1. <componentSets>
Each componentSet element is used to configure a component
set, and each component set can reference multiple service components.
2. <providerSets>
Each providerSet element is used to configure a provider
set, and each provider set can reference multiple service providers.
3. <components>
Each of these component elements is used to configure
a specific service component.
4. <providers>
Each of these provider elements is used to configure
a specific service provider.
System config file
The iserver-system.xml contains the configuration information
of the system, the root node is the < server > element, and the
< server > node currently mainly contains <properties> 、<management>、<hosts>、<clustering>、<harLog>、<queryFilter>
child node elements.
1. < properties > element
It is used to set global attribute information in the
SuperMap iServer configuration system, such as the default output path
of the service, the access site, and the setting of whether to check the
environment:
- < output path >: output path whose value
is ../webapps/iserver/output. When the cache image output path is
not specified for a specific service, SuperMap iServer assumes the
default value.
- < outputSite >:
output site, which is the root directory for accessing cached images
URI whose value defaults to HTTP://{IP}:{port}/iserver/output/. When
an image publishing site is not specified for a specific service,
SuperMap iServer assumes the default value. If HTTPS encrypted communication
is enabled, this value needs to be changed to HTTPS://{IP}:{port}/iserver/output/.
- < realspaceSecurityEnabled >: realspace
security controls whether to enable, default is true.
- < realspaceCacheAccessKey >: 3D data
password.
- < envCheckEnabled >: Set whether to perform
environment check. The default value is true.
- < restartWhenCrash >: whether to restart
the service automatically after the service is shutdown abnormally.
The default is true.
- <
checkdatasourceconnectioninterval>:The time interval to check whether
the database type workspace is changed, whether the database type
datasource is disconnected, or whether the dataset in the PostGIS
service used as a data source for service publishing has changed.
The unit is second. If it is less than or equal to 0, it means never
check. The default is 30 seconds. It is recommended that you set this
parameter ro a value greater than or equal to 30, otherwise the check
will be too frequent and may cause data queries to get stuck.
- < refreshDatasource >: Set whether to
enable refreshing database type, including database datasources in
the workspace and PostGIS service used as a data source for service
publishing. The default is false, that is, it is not enabled. Need
to used with checkDatasourceConnectionInterval. Takes effect when
the checkDatasourceConnectionInterval value is greater than 0 and
refreshDatasource is true.
- < {iServerData1} >, < {iServerDataPath1}
>: a variable that represents a workspace path or path. See the
default local workspace path for details.
- < enableSQLFilter >: Whether to enable
SQL injection detection. The default is false. This parameter is supported
by the SQL query of the featureResults subresource under the data
resource and all queries of the queryResults subresource under the
map resource.
-
< deniedFiles >: Upload internal file formats that are prohibited
when zip files, Internal file types prohibited by default are: <
deniedFiles >.jsp.sh.exe.bat.html.js.war.class.jar.shtml.htm.php.aspx.asp.asa.jspx,.cgi<
deniedFiles >. Modifying this configuration requires a reboot for
the iServer to take effect. (Obsolete)
- <checkServiceStorageConnectionInterval>:The
time interval for checking whether the database of storage service
configuration information is disconnected, in seconds. < = 0 means
never check; when the value is greater than 0 and less than 20, check
at the time interval of 20 s.
The global attributes outputPath and outputSite can
also be accessed through the service manager Web Manager. Please refer
to the global attribute
setting .
- < encryptionAlgorithm >: Configure to
use AES/GCM/NoAdding for encryption, with a value of AES. If no configuration
or other items are configured, DESede encryption will be used by default.
- < maxFeatureWriteThreadCount >: Maximum
number of concurrently accessed threads for the configuration the
data service providers (optional), default is 1, that is, the maximum
number of threads accessed concurrently is 1. You can adjust this
value according to the available resources of the server. Note that
this parameter should be less than maximum number of connections to
the database in use. Note that when this parameter is configured in
both the system.xml and the service providers, the configuration in
the provider takes precedence.
- < writePermitTimeout >: Timeout for waiting
for write permission of configuration the data service providers (optional),
in seconds, default is 120, that is, if the waiting time for obtaining
write permission is greater than 120 seconds, it is a timeout. Note
that when this parameter is configured in both the iserver-system.xml
and the service providers, the configuration in the provider takes
precedence.
- < poolSize >: Configure the thread pool
size of map service providers (optional). The default is 1.
- < maxAttachmentSize >: Configure the
maximum limit of attachment files uploaded when modifying elements
in data services. The unit is M, the default value is 100, and the
value range is a positive integer.
- < tokenName >: Configure the name of
the iServer key. The default name for the system is' token '. You
can configure it with a different name according to your project needs.
After the configuration is complete, you need to restart iServer for
it to take effect. For the use of token, please refer to: based
on Certification of Token .
- < forceStop >: Whether to forcibly stop
iServer after enabling resources recovery regularly. The parameter
is true indicates that the iServer will be forced to stop. The default
is false.
- < fastjson.autotype.allowPrefixs >: Use
custom extension classes (type names not prefixed with com.supermap)
and cannot serialize Alibaba fastjson correctly, the type name prefix
of autotype can be added by customization. Setting multiple prefixes
is supported. Use ";" separation, such as com.huawei; com.apache.
- <returnSmgeometryField>: Used to control
whether the smgeometry field is included in the response body field.
The default is false, that is, this field is not returned. The affected
resource response bodies include: fieldnames and fieldValues in the
features of the query result returned by the featureResults resource
POST request; fieldNames and fieldValues in the features of the result
returned by the feature resource GET request; fieldNames and fieldValues
in the recordset of the result returned by the datasetBufferResult
resource GET request.
- < fileManagerWorkDir >: The file management
directory can be browsed and uploaded by iServer and iEdge systems.
If not set, there is no limit to the file directory range, and it
defaults to empty. When
configured, the file selector can only access subdirectories of that
path, and the value returned is a path that begins with a placeholder,
such as ${fileManagerWorkDir}/sample/data/China/China100.smwu; It
can only be uploaded to this directory. It can only be uploaded to
this directory. When using a relative path as the path parameter,
it is created in the directory specified by the root directory fileManagerWorkDir.
Note:
1. When this parameter is configured by way of an environment variable,
its value can no longer be modified by the config file. 2. When using
the Windows version, if garbled characters appear by setting the FILEMANAGERWORKDIR
environment variable with Chinese characters in startup.bat, add chcp 65001 and chcp 936 before and
after it. Please refer to the
custom configuration file management root directory for detail.
3. Changing the root directory configuration
will affect the normal use of the published services. The following
operations are required according to different situations: if the
root directory has been set, the original directory file needs to
be manually migrated to the new directory and the directory tree structure
of the original file needs to be retained; if the root directory setting
needs to be cancelled, the placeholder in the config file needs to
be manually replaced. ${fileManagerWorkDir } is the actual path. 4.
This modification will not take effect until iServer and iEdge are
manually restarted. 5. After initialization, iEdge can only be modified
by this setting in the modify configuration file.
- <forceShutdownSeconds>:
This configuration refers to the mandatory process shutdown function,
with units in seconds, and the default si 30. Wher the value is 0
or not configured, it indicates that the function is enabled. and
the value is the waiting time for mandatory process shutdown. After
enabling, executing shutdown.sh or shutdown.bat will force shut down
all processes related to SuperMap iServer. Note that the war package
does not have this configuration item, which means this function is
disabled.
- <disableFieldNameToUpperCase>: Whether
to disable conversion of field names in Data Services to upper case,
default is false, which means disabled. Note:
Setting the UGC Data Provider value to false through the Service Provider
configuration does not take effect when the global setting value is
true. However, when the global setting value is false, if the value
in Service Provider is true, field names will be able to converse.
- <license.client.session.timeout>:
The expiration time of the client access session, the default value
is 5, in minutes. When the iServer Standard (Limit 3 clients) Edition
or Standard (Limit 10 clients) Edition licenses is activated, the
configuration takes effect. If the user client is not accessed iServer
for more than this time, the client will be forced offline.
2. < uploadFileSetting > element
It is used to uniformly set the relevant configuration
of SuperMap iServer file upload, such as the maximum volume of the uploaded
file, the maximum volume after decompression, whether the file with the
same name is overwritten, and the storage directory:
- < uploadSize >: refers to the maximum
size of the uploaded file. It is 2048 MB by default. Positive integer
is supported, and the unit is Mb. If this value is not set, it will
be regarded as unlimited.
- < uploadUnzipSize >: The maximum size
of the uploaded file after decompression. It is 5120MB by default.
Positive integer is supported. The unit is Mb. If this value is not
set, it is regarded as unlimited.
- < uploadOverwrite >: Whether to overwrite
the uploaded file with the same name. The default is no.
- < uploadDir >: the directory where the
uploaded files are stored. When configured, the file selector can
only access subdirectories of that path, and the value returned is
a path that begins with a placeholder, such as ${uploadDir}\sample\data\China\China100.smwu.
Priority: fileManagerWorkDir > uploadDir. (Obsolete)
- < deniedFiles>: Internal file formats
that are not allowed when uploading zip files, internal file types
prohibited by default are: < deniedFiles >.jsp.sh.exe.bat.html.js.war.class.jar.shtml.htm.php.aspx.asp.asa,.jspx,.cgi<
deniedFiles >. Modifying this configuration requires a reboot for
the iServer to take effect.
3. < management > element
Metadata info for configuring SuperMap iServer. The
metadata info of iServer contains service component type metadata (<
component-types >), the provider type metadata (< provider-types
>) and service interface type metadata (< interface-types >),
and the security config (< security >).
An example of a security config node is as follows:
<security>
<accessControl>
<SecuritySetting>
<!-- Verification code configuration, default is turned off -->
<captchaConfig>
<enable>false</enable>
<type>IMAGE_CAPTCHA</type>
<length>4</length>
<expireInSeconds>120</expireInSeconds>
</captchaConfig>
<isSecurityEnabled>true</isSecurityEnabled>
<disableRememberMe>false</disableRememberMe>
<cacheInfoToMemory>true</cacheInfoToMemory>
<tokenKey>4da7ef8f2e734f56ab2ecfae20cce49a</tokenKey>
<PBKDF2Iterations>1000</PBKDF2Iterations>
<!-- Password anti brute force cracking settings -->
<passwordProtectedSetting>
<passwordDiffCount>5</passwordDiffCount>
<userPasswordErrorCounterSetting>
<passwordErrorProtectEnable>false</passwordErrorProtectEnable>
<lockedTime>1200000</lockedTime>
<periodLength>600000</periodLength>
<allowFailCountPerPeriod>5</allowFailCountPerPeriod>
</userPasswordErrorCounterSetting>
</passwordProtectedSetting>
<!-- Three segment root key configuration -->
<rootSecretKeySetting>
<loadModelType>TRIPART</loadModelType>
<part3>[B@7e31062c</part3>
</rootSecretKeySetting>
</SecuritySetting>
</accessControl>
<!-- Security Information Storage Configuration -->
<storage class="com.supermap.server.config.SQLSecurityInfoStorageSetting">
<type>MYSQL</type>
<connInfo>
<username>root</username>
<password>super123.</password>
<dbType>MYSQL</dbType>
<driverClass>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driverClass>
<jdbcUrl>jdbc:mysql://192.168.120.44:3306/supermap?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8</jdbcUrl>
<maxPoolSize>30</maxPoolSize>
<initialPoolSize>5</initialPoolSize>
<minPoolSize>5</minPoolSize>
<maxIdleTime>0</maxIdleTime>
<maxWait>3000</maxWait>
</connInfo>
</storage>
<!-- iServer built-in session configuration -->
<session class="com.supermap.server.config.BuildInSessionSetting">
<type>BuildIn</type>
<timeout>10000</timeout>
<checkLoggedInAnotherPlace>true</checkLoggedInAnotherPlace>
<loggedInAnotherPlaceProcessingStrategy>Notifying</loggedInAnotherPlaceProcessingStrategy>
</session>
<!-- iServer encryption algorithm and specification configuration -->
<encryption class="com.supermap.server.config.EncryptionSetting">
<serviceKeySettings>
<serviceKeySetting>
<keyID>keyIDNAME</keyID>
<version>1.1</version>
<algorithm>AES</algorithm>
<keyLength>256</keyLength>
<attributes>abcd</attributes>
</serviceKeySetting>
</serviceKeySettings>
</encryption>
</security>
Among,
-
< captchaConfig >: used to set the verification code when logging
in. It is closed by default. The specific parameters include:
- < enble >: Whether to enable the login
verification code
- < type >: verification code type. Currently,
only image verification code (IMAGE_CAPTCHA) is supported.
- < expireInSeconds >: verification code
expiration time, in second
- < length >: length of the generated image
verification code
- < isSecurityEnabled >: Used to set whether
to enable security control;
- < managementEnabled >: Used to set server
management related capabilities. The default is true, when false,
all administrative capabilities are disabled
- < PBKDF2Iterations >: Used to set the
number of iterations of the PBKDF2 password encryption algorithm.
iServer takes effect after enabling PBKDF2 encryption; The larger
the number of iteration, the longer it takes to log in.
- <
tokenKey >: used to set the shared key of Token;
-
< disableRememberMe >: used to set whether to disable the "Remember
Me" function on the login page. The default value is false, that
is, the "remember me" function is available. This configuration
item needs to restart the iServer to take effect.
- < cacheInfoToMemory >: Used to set whether
to cache all user information in memory and query user information
from memory. The default is True, indicating that all user information
is cached in memory. If the number of users is relatively large, it
is recommended to set it to false. The user information is not cached
to the memory, but queried from the database in real time, because
caching all user information requires a large amount of SQL query,
slow performance, only query the relevant data in the specific query;
- < passwordProtectedSetting >: Used to
set password protection to prevent brute force attack. The specific
parameters include:
- < passwordDiffCount >: The password cannot
be repeated with the previous N times. The default is 5 times.
- < userPasswordErrorCounterSetting >:
This includes the 'passwordErrorProtectEnable' parameter that determines
whether password anti brute force cracking is enabled, as well as
the allowed number of consecutive failures within a time period ('periodLength',
default 6000000 milliseconds, or 10 minutes) ('allowFailedCountPerPeriod',
default 5 times), and the automatic unlocking time ('lockedTime',
unit: milliseconds, default 1200000, or 20 minutes).
- < rootSecretKeySetting
>: Root Key Configuration. The configuration needs to be configured
in the iServer before it is initialized for the first time, otherwise
it will not take effect. Specific parameters include:
- < loadModelType >: root key type, including
KEYSTORE mode and TRIPAR T three-part. The default value is KEYSTORE.
The TRIPART three-segment root key is dynamically generated by the
combination of the three-segment keys part1, part2, and part3.
- < part3 >: The third key, which is generated
by secure random number by default when iServer is started. It is
available when the root key type is TRIPART.
- < encryption >: used to set the encryption
algorithm and specification. Currently, the configuration of GIS service
encryption algorithm settings and external key settings are supported.
For details, see: Encryption
Algorithm Configuration.
- < storage >: Used to set the storage
location of security information, including the < type > field
used to specify the storage type. Currently, SQLITE, MYSQL, PostgreSQL,
Kingbase, GaussDB, Vastbase, GBase are supported. And < connInfo
> of the configuration the data library connection info. Taking
MYSQL database as an example, the specific parameters of connection
info include:
- < driverClass >: The connection driving
class of the database, which is the com.mysql.jdbc.Driver.
- < jdbcUrl >: Connect to database-driven
URL connection in the form jdbc:mysql://{ip}:{port}/{database}?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8.
Where {IP} is the IP address of the machine where it is located, {port}
is the service port of MySQL, which is 3306 by default, and {database}
is the name of the database, which can be set as the database you
have created to store user information. These parameters you can use
according to your installed MySQL to configure the actual situation.
- < username >: The user name. A user with
access to the database {database}.
- < password >: The password for the user.
- < initialPoolSize > The size of the connection
pool to initialize, that is, the number of connections to initialize.
The default value is 5.
- < maxPoolSize >: The maximum number of
active connections provided by the connection pool at one time. You
can base on This value is based on the performance of the MySQL server
and defaults to a maximum of 30 active connections.
- < minPoolSize >: The minimum number of
active connections provided by the connection pool at one time. The
default value is 5.
- < maxIdleTime >: waiting time of idle
connection, that is, the time that can be reserved when the current
connection is idle, in milliseconds. If there is no operation after
this time, the current connection will be closed automatically. The
default value is 3000. If set to 0, an idle connection is always retained.
- < maxWait >: wait time for abnormal connection,
that is, the waiting time for abnormal connection, in milliseconds.
If the abnormal connection is not restored within this time period,
the current connection will be closed automatically. The default is
the 300000.
- < useStoredAdmin >: Two options for the
case where the initialization administrator (for example, admin1)
is already stored in the database: if the default is False, the initialization
administrator (admin 2) of the current iServer will be used. Also
overrides the initialization administrator stored in the database
(the administrator stored in the database is overwritten with Admin
2); if True, the initialization administrator already stored in the
database (admin 1) will be used instead of the administrator of the
current iServer (for example: admin 2).
- < session >: used to set session configuration
information such as storage location of session information and session
timeout time. Currently, there are seven optional configuration modes
supported: iServer built-in session, Redis session, PostgreSQL session,
Kingbase session, GaussDB session, Vastbase session, and GBase session.
You can select one of them for configuration.
1) For iServer built-in sessions, the specific configuration parameters
include:
- < type >: session type. The default value
is BuildIn, which indicates the built-in session of iServer.
- < timeout>:iServer
Built-in session timeout configuration, that is, the idle time after
logging in the iServer, in milliseconds. After the timeout, the session
ends and the iServer logout. This configuration takes effect only
when the remote login alarm is enabled, that is, set < checkLoggedInAnotherPlace
> to true.
- < checkLoggedInAnotherPlace
>: whether to enable remote login alarm, true indicates that the
remote login alarm is enabled, and the default is false. After configuration,
the iServer needs to be restarted to take effect.
- < loggedInAnotherPlaceProcessingStrategy
>: remote login processing strategy, setting < checkLoggedInAnotherPlace
> as true for this configuration to take effect. Optional values
include: Notifying, LatestLoggedInFirst, Notifying, which means that
the same account can log in to multiple hosts at the same time, and
will notify the current detection of the remote login of the account
when logging in; LatestLoggedInFirst, the latest login has priority,
which means that the same account can only log in to one host at the
same time, and the currently detected remote login will also be notified
when logging in. Unlike the notification mode, the account that was
last logged in on another host is automatically logged out. If remote
login is enabled, configure CheckLoggedInAnotherPlace as true, but
the remote logon processing policy is not configured. The Notifying
mode is used by default.
2)For
Redis sessions, specific configuration parameters include:
- < type >: session type, set to Redis.
- < host >: IP of the machine where the
Redis database is located.
- < port >: The port number of the Redis
database service.
- < user >: Redis database user name.
- < password >: Redis database password.
- < MaxActive >: that maximum number of
active connections provide by the connection pool at any one time.
- < maxIdle >: The maximum number of idle
connections. The maximum number of idle connections to the database.
- < maxWait >: When there is no available
connection, the maximum wait time is in milliseconds, and an exception
will be thrown after timeout.
- < timeout >:
The idle time after the client connects to the database, in milliseconds.
After the timeout, the connection is disconnected.
- < testOnBorrow >: When the connection
is used, check whether the connection is available; if it is true,
the resulting connection is available.
- < checkLoggedInAnotherPlace >: whether
to enable remote login alarm, true indicates that the remote login
alarm is enabled, and the default is false.
- < loggedInAnotherPlaceProcessingStrategy
>: remote login processing strategy, setting < checkLoggedInAnotherPlace
> as true for this configuration to take effect. Optional values
include: Notifying, LatestLoggedInFirst. Notifying, which means that
the same account can log in to multiple hosts at the same time, and
will notify the current detection of the remote login of the account
when logging in; LatestLoggedInFirst, the latest login has priority,
which means that the same account can only log in to one host at the
same time, and the currently detected remote login will also be notified
when logging in. Unlike the notification mode, the account that was
last logged in on another host is automatically logged out. If remote
login is enabled, configure CheckLoggedInAnotherPlace is true, but
the remote logon processing policy is not configured. The Notifying
mode is used by default.
3)For PostgreSQL session,
Kingbase session, GaussDB session, Vastbase session, and GBase session,
take PostgreSQL as an example, specific configuration parameters include:
- <type>: session type, set to PostgreSQL.
- <checkLoggedInAnotherPlace>: whether
to enable remote login alarm, true indicates that the remote login
alarm is enabled, and the default is false. After configuration, you
need to restart the iServer to take effect.
- <timeout>: The idle time after the client
connects to the database, in milliseconds. After the timeout, the
connection is disconnected.
- <jdbcUrl>: The service address, set format:
jdbc:posrgresql://{ip}:{port}/{database}
- <tableName>: The PostgreSQL database
session information storage table name.
- <user>: PostgreSQL database user name.
- <password>: PostgreSQL database password.
- <schemaName>: The PostgreSQL database
schema name.
- <maxPoolSize>: The maximum number of
active connections that a database connection pool can provide at
the same time. The default value is 50.
- <minPoolSize>: The minimum number of
active connections that a database connection pool can provide at
the same time. The default value is 10.
- <initialPoolSize>: The initial connection
pool size, which is the number of connections initialize. The default
value is 50.
- <maxIdleTime>: The wait time for an idle
connection, in milliseconds. If no operation is performed within
the configured time, the current cinnection will be automatically
closed. The default value is 3000. If set to 0, idle connections will
be retained permanently.
- <maxWait>: The wait time of the system
when a connection is abnormal. in milliseconds. If the connection
exception is not restored within the configured time, the current
cinnection will be automatically closed. The default value is 3000.
3. < hosts > element
Host used to configure the SuperMap iServer service.
Can contain multiple < host >, one host is:
<host port="8090" type="webapp" uriBase="/services">
<interface-type>com.supermap.services.wms.WMSServlet</interface-type>
<interface-type>com.supermap.services.rest.RestServlet</interface-type>
<interface-type>com.supermap.services.wfs.WFSServlet</interface-type>
<interface-type>com.supermap.services.wmts.WMTSServlet</interface-type>
</host>
Where, < interface-type > represents the service
type contained in the service host, and the attributes of < host >
have the following meanings:
- The port attribute is the port number of the
service host through which the user accesses the services and servlets
contained in the service host. The port number of the container is
consistent and is synchronized with the port number of the servlet
container in real time when the SuperMap iServer service is accessed.
- The type attribute is the type of the service
host. "Webapp" indicates that this is a Web Service, and
it can also take values RMI, which represents the other host type.
- The uriBase attribute, the root path of the
service host, from the root directory of the servlet.
4. < clustering > element
Including applications such as cluster configuration.
For details on the elements related to cluster subnodes, refer to Managing
a Cluster with a config file in the Cluster topic.
5. < harLog > element
It is used to configure the service access logs, such
as whether to enable service access logs, the file name of the service
access logs, and the settings of the monitored service URI address:
- < enabled >: Set whether to enable service
access logs. The default is false.
- < name >: The file name of the output
service access logs. The default name is iServerHTTPArchive, which
supports user customization.
- < monitorURLs >: The monitored URL address
of the SuperMap iServer service.
6. < queryFilter > element
Used for filtering configuration of attributeFilter
parameter in SQL query to prevent SQL injection. SQL Injection refers
to the process of deceiving the server to perform malicious operations
by inserting illegal strings or strings against the user's wishes into
the SQL query expression during the SQL query of data or map.
- < enabled >: Set whether to enable SQL
query filtering. The default is false. When enabled is true, four
types of expressions, including constant expression, constant equivalent
expression, constant IN expression, and constant constant expression,
will be disabled by default. In addition, some threat characters will
be disabled by default, including exec、insert、delete、update、join、union、master、truncate。
In addition to the above expressions and strings that are disabled
by default, you can also pass the filterString parameter sets other
strings that need to be disabled in the SQL query.
- < filterString >: Set the character string
to be filtered by SQL query. Support any character string (data manipulation
language (DML), expression, wildcard, special character, etc.), separated
by semicolons, such as: set <filterString>delete;SMID=.</filterString>.
When users perform SQL queries on data or maps, if the string 'delete
or SMID=any value' appears in the SQL query expression, the system
will assume that the query expression is illegal and return a 400
parameter exception to prevent malicious SQL commands from being executed,
thereby protecting the user's data security. If SQL query filtering
strings are not set, semicolons will be masked by default in SQL query
expressions. This configuration item will take effect upon saving,
without the need to restart iServer
- <attributeFilterNotNull>:When performing
SQL queries, whether the attributeFilter parameter cannot be null
(i.e., the parameter value is null, "", '' or left blank).
The default is true, and it takes effect when the SQL injection prevention
configuration is enabled, i.e., when the <enabled> is true.
7. <repository>
Used to set the storage location of a temporary resource.
For detailed information, refer to Lifecycle
of Temporary Resources .
8. < relayService > element
Trunking service configuration for iEdge. Used in iEdge
products only.
- < enabled >: Whether to enable the relay
service.
- < isLocalPriority >: Whether the local
service is preferred for the service with the same name. If it is
true, the local service will be used first, and the service with the
same name in the relay server will be hidden; if it is false, the
relay service will be used first, and the service with the same name
in the local server will be hidden.
- < remoteServices >: The address of the
remote service list in the relay service, such as http://<server>:<ip>/iserver/services.
- < updateInterval >: The time interval
for the relay service to be dynamically updated. If there is a change
in the remote service list, the relay service will be dynamically
updated according to this time interval. The unit is milliseconds
(ms), and the default is 60000ms.
9. < license > element
It is used to save the license information of the current
iServer, including the version in use and the extended service license.
See Selecting
Licenses in iServer . Examples are as follows:
<licenseMode>DefaultLicense</licenseMode>
<license>
<enabledmodules>
<string>ENTERPRISE</string>
<string>CHART</string>
<string>NETWORK</string>
<string>SPACE</string>
<string>SPATIAL</string>
<string>TRAFFIC_TRANSFER</string>
<string>PLOT</string>
<string>SITUATIONEVOLUTION</string>
<string>SPATIAL_PROCESSING</string>
<string>GEO_BLOCKCHAIN_SERVICE</string>
<string>SPATIAL_STREAMING</string>
<string>MACHINE_LEARNING_SERVICE</string>
<string>IMAGE_SERVICE</string>
</enabledmodules>
</license>
Among,
- < License Mode > is used to set the license
type, including normal license (DefaultLicense) and Web License (Web
License) and Cloud License (Cloud License).
- < enabledmodules > contains the license
names used, including:
- "ENTERPRISE":Advanced
- "STANDARD":Standard
- "CHART": Chart Service Extension
Module
- "NETWORK": Network Analysis Service
Extension Module
- "SPACE": 3D service extension
- "SPATIAL": spatialanalyst service
extension
- TRAFFIC_TRANSFER ": Traffic Transfer Service
Extension Module
- SPATIAL_STREAMING ": stream processing
model extension
- SERVICE_NODE_ADDITION ": service node
extension
- "PLOT": plot service extension module
- SPATIAL_PROCESSING ": distributed analyst
service extension
- "SITUATIONEVOLUTION": situation deduction
service extension module
- MACHINE_LEARNING_SERVICE ": machine learning
service extension
- IMAGE_SERVICE ": image services extension
- "THREEDDESIGNER_SERVICE": 3D Geodesign
Service Extension "
The name of the extension by core module is the name
of the original extension module followed by the number of cores. For
example, the name of the machine learning service (16 cores) expansion
module is' MACHINE_LEARNING_SERVICE_16CORES '. The name of the machine
learning service (32 cores) expansion module is' MACHINE_LEARNING_SERVICE_32CORES
'.
10. < multiworkers > element
Information used to configure the multi-process service.
Such as the number of processes, port range, etc. Examples are as follows:
<multiworkers>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<workerCount>4</workerCount>
<workerIP>127.0.0.1</workerIP>
<workerPortStart>8900</workerPortStart>
<workerPortEnd>9000</workerPortEnd>
<workerBaseDir>../../workers</workerBaseDir>
<xmx>1024m</xmx>
<communicationPort>8100</communicationPort>
<requestDispatchMode>RANDOM</requestDispatchMode>
<timeout>20</timeout>
</multiworkers>
The specific parameters are described as follows:
- < enabled >: whether to enable multi-process
mode.
- < workerCount >: Number of processes.
- < workerIP >: Set the communication IP
between the main process and the child process.
- < workerPortStart >: The start port number
of the Workerprocess port range.
- < workerPortEnd >: The end port number
of the Worker process port range.
- < workerBaseDir >: The working directory
of the child process.
- < xmx >: Java virtual machine memory
settings.
- < communicationPort >: Set the communication
port number between the main process and the child process.
- < requestDispatchMode >: The master node
forwards the request mode to the child node. Including: RANDOM, representing
random patterns; TO_LEAST_REQ indicates that the master node will
forward the request to the child node with the smallest number of
requests processed.
- < timeout >: Specifies the timeout for
the master node to forward requests to the child nodes.
- < workerRecycle
>: Automatically recycles the worker process.
- < enabled >: Whether to enable automatic
recycling. The default value is false.
- < checkPeriodHours >: polling time interval
of working process resource usage. The unit is hour and the default
is 24 hours.
- < maxWaitDisposeSeconds >: The maximum
wait time for the worker process during destruction. If a worker process
is in the process of recycling and destroying, and the duration exceeds
the set value, the process will be automatically destroyed. The unit
is second, the default 120 seconds.
Note:
After modifying parameters related to multiple processes (excluding
workerCount), it is necessary to manually restart iServer to take effect.
11. < scheduledTasks > element
Used to set timing-related tasks, such as server config
file scheduled backup, resources recovery regularly, etc. Examples are
as follows:
<scheduledTasks>
<scheduledRestart>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<restartTime>
<hour>9</hour>
<minute>35</minute>
</restartTime>
<dayOfWeek>1,2,3,4,5,6,7</dayOfWeek>
<restartDate>2023-11-1</restartDate>
</scheduledRestart>
<scheduledBackup>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<backupTime>
<hour>10</hour>
<minute>40</minute>
</backupTime>
<dayOfWeek>1,2,3</dayOfWeek>
<backupDate>2023-11-1</backupDate>
</scheduledBackup>
</scheduledTasks>
The specific parameters are described as follows:
- < scheduledRestart > is used to set the
server resources recovery regularly, including:
- < enabled >: whether to enable server
resources recovery regularly.
- < restartTime >: Recycle time. Its child
parameter hour is used to set the hour value of the specified recycling
time, minute is used to set the minute value.
- < dayOfWeek >: Set the recycling time
as an interval. This parameter is used when resources need to be reclaimed
on the appointed day of each day or week, and cannot be set at the
same time as the < restartDate > parameter. Enter a number to
represent the week of the week, separated by commas. For example,
if it is necessary to carry out regular collection every day, set
the parameter to 1,2,3,4,5,6,7.
- < restartDate >: Set the recycle time
as appointed day. This parameter is used when resources need to be
reclaimed on the appointed day of a certain day, and cannot be set
at the same time as the < dayOfWeek > parameter. Example: 2023-11-1
-
< scheduledBackup > Used to set the server config file scheduled
backup, specifically including:
- < enabled >: whether to enable server
config file scheduled backup.
- < backupTime >: The backup time. Its
subparameter hour is used to set the hour value of the specified backup
time, minute is used to set the minute value.
- < dayOfWeek >: Set the backup time as
interval. This parameter is used when the config file needs to be
backed up on the appointed day of every day or week. Enter a number
to represent the week of the week, separated by commas. For example,
if scheduled backup is required every day, set the parameter to 1,2,3,4,5,6,7.
The < backupDate > parameter value takes effect when set with
the < backupDate > parameter.
- < backupDate >: Set the backup time in
the appointed day mode. This parameter is used when the config file
needs to be backed up on the appointed day of a certain day. For example:
2023-11-1. The < backupDate > parameter value takes effect when
set with the < dayOfWeek > parameter.
12. < spark > Element
Spark cluster basic configuration:
- < sparkHome >: Spark installation directory.
- < masterAddress >: Master node address
of the Spark distributed cluster.
13. < processing > element
For distributed analyst service configuration, the
following is an example:
<processing>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<referToken>Token</referToken>
<referServicesAddress/>
<xmx>1024m</xmx>
<workerPort>6765</workerPort>
<defaultOutputType>UDBX</defaultOutputType>
<rddStorageCount>10</rddStorageCount>
<buildPyramid>false</buildPyramid>
<publishService>true</publishService>
</processing>
The specific parameters are described as follows:
- < enabled >: whether to enable distributed
analysis service. True means that the function is enabled, false indicates
that the feature is turned off
- < referToken >: tocken information of
the user with publish services permission of associated server address
- < xmx >: JVM maximum heap size, 1024m
by default
- < workerPort >: process port number
- < defaultOutputType >: default analysis
result output type
- < rddStorage Count >: Number of rdd storage
- < BuildPyramid >: The vector pyramid
is enabled within the distribution, and the default is false, that
is, it is closed.
- < publishService: Whether to publish the
analysis result as data and map services. The default is true
.
Note:
Suggest adding the SparkSessionNoRebuild switch for configuration. After
enabling this switch, the system will not automatically rebuild SparkSession
upon detecting Spark service restart, thus avoiding related errors. Configuration
method: In <processing> node, add <sparkSessionNoRebuild>true</sparkSessionNoRebuild>.
Then restart iserver, and after restarting, iserver.rog will display "SparkSessionNoRebuild
is set to true", indicating successful setting.
14. < serviceInstanceManager > element
Used for dynamic management configuration of service
instance. The example is as follows:
<serviceInstanceManager>
<enableLazyInitService>true</enableLazyInitService>
<idleDispose>
<enable>true</enable>
<checkPeriod>30000</checkPeriod>
<maxIdleTime>30000</maxIdleTime>
</idleDispose>
<capacityLimit>
<enable>true</enable>
<maxInstanceCount>2000</maxInstanceCount>
</capacityLimit>
</serviceInstanceManager>
Among,
- < enableLazyInitService >: whether to
enable the dynamic management of service instances. True indicates
that the function is enabled. After setting, the service will not
be initialized and started immediately when the iServer is started.
False indicates that the function is disabled. After setting, the
service will be started in the iServer. The service will be initialized
and started immediately at startup, and the following parameters will
not take effect.
- < idleDispose >: idle service related
settings, including service status patrol interval and idle service
active destruction time.
- < enable >: Whether to enable idle service
related settings. True means enabled. At this point, you can modify
the checkPeriod and maxIdleTime parameters to the expected values
that match the actual application scenario. False indicates shutdown,
and the checkPeriod and maxIdleTime parameters will be set to default
values of 30000 (ms) and 300000 (ms), respectively, and cannot be
modified.
- < checkPeriod >: service status patrol
interval, in milliseconds, the default value is 30 seconds. Note that
the smaller the value, the more frequent the patrol, the more accurate
the behavior of automatic destruction of idle services, but at the
same time the more computer resources are consumed.
- < maxIdleTime >: the active destruction
time of the idle service. If a service's idle time exceeds this threshold,
it is automatically destroyed. The unit of this parameter is millisecond,
and the default value is 5 minutes.
- < capacityLimit >: Service quantity limit
setting, including the maximum number of online service instances.
- < enable >: Whether to enable the service
quantity limit setting. True means enabled, at which point you can
modify the maxInstanceCount parameter to the expected value that matches
the actual application scenario. False means closed, and the maxInstanceCount
parameter will be set to the default value of 2000 and cannot be modified.
- < maxInstanceCount >: The maximum number
of online service instances, 2000 by default. When the number of simultaneously
online services exceeds this value and a new service is requested,
the relevant service will not be started. The iServer will report
an error.
15. < storages > element
Used for the management configuration of
the distributed image tile library, the example is as follows:
<storages>
<storage>
<id>smtiles</id>
<tileSourceInfo class="com.supermap.services.tilesource.MongoDBTilesourceInfo">
<datastoreType>TILES</datastoreType>
<type>MongoDB</type>
<readPreference>primary,nearest,secondary</readPreference>
<serverAdresses>
<string>172.16.120.199:27017</string>
</serverAdresses>
<database>smtiles</database>
</tileSourceInfo>
</storage>
</storages>
Among,
- < storage >:
Distributed tile library storage information.
- < ID >: Store
ID.
- < tileSourceInfo
>: Tile source connection info.
- <datastoreType>:datastore type
- <type>:enginetype
- < readPreference
>: When the database is MongoDB, you can set the read policy, including
primary, primaryPreferred, secondary, secondaryPreferred, and nearest.
- < serverAdresss >: service address, including
IP and port.
- <database>:name
16. < serviceStorage > element
Used for the management configuration of
the distributed image tile library, the example is as follows:
<serviceStorage>
<connInfo>
<username>name</username>
<password>password</password>
<dbType>HIGHGO_DB</dbType>
<driverClass>com.highgo.jdbc.Driver</driverClass>
<jdbcUrl>jdbc:highgo://172.16.121.157:5866/highgo</jdbcUrl>
<maxPoolSize>30</maxPoolSize>
<initialPoolSize>5</initialPoolSize>
<minPoolSize>5</minPoolSize>
<maxIdleTime>600</maxIdleTime>
<maxWait>3000</maxWait>
</connInfo>
<type>HIGHGO_DB</type>
<tableName>iserver_v1_services</tableName>
<metaTableName>iserver_v1_metainfos</metaTableName>
<eventLogTableName>iserver_v1_eventLog</eventLogTableName>
<patrolTime>5</patrolTime>
<schemaName>test</schemaName>
</serviceStorage>
Among,
- <connInfo>:Database
connection information, including the user name , password, database
type name, database connection address and other basic information
of the database.
- <username>:The user with database access.
- <password>:The password of the user.
- <dbType>: Database type, including GaussDB,
GBASE8C, HIGHGO_DB, Kingbase, ORACLE, POSTGRESQL, Vastbase.
- <driverClass>: The database driver
supports using the database.
- <jdbcUrl>: The url which is able
to connect to the database.
- <maxPoolSize>: The maximum number of
active connections that a database connection pool can provide at
the same time.
- <minPoolSize>: The minimum number of
active connections that a database connection pool can provide at
the same time.
- <initialPoolSize>: The initial connection
pool size, which is the number of connections initialize.
- <maxIdleTime>: The wait time for an idle
connection, in milliseconds
- <maxWait>: The wait time of the system
when a connection is abnormal. in milliseconds
- <type>: Database
type, including GaussDB, GBASE8C, HIGHGO_DB, Kingbase, ORACLE, POSTGRESQL,
Vastbase.
- <tableName>:
Table name for service storage. The name of the table that stores
the service configuration information is iserver by default when configured
by the service management UI, and the corresponding configuration
information is iserver_v1_services.
- <metaTableName>:
Table name for meta information. It is iserver by default when configured
by the service management UI, and the corresponding configuration
information is iserver_v1_metainfos.
- <eventLogTableName>:
Table name for event log. It is iserver by default when configured
by the service management UI, and the corresponding configuration
information is iserver_v1_eventLog.
- <patrolTime>:
Database patrol interval. The unit is seconds, and the default value
is 5.
- <schemaName>:
The schema where the storage service configuration information table
is located, dafault stored in the public mode. If you need to store
the service configuration information in a non-public mode of the
database, configrue the specified schema name.
Datastore config file
Datastore config file iserver-datastores.xml, root
node is < application > elements, including < datastores >
child node elements, where each datastore element is used to configure
a specific datastore and contains the following attributes:
- datastoreType:datastore type.
- type:data type
- Name: data name
- URL: Datastore directory
- commonsCSVMetaData:csv file metadata info
Examples are as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<application>
<datastores>
<datastore>
<datastoreType>BIGDATAFILESHARE</datastoreType>
<type>FOLDER</type>
<name>samples</name>
<url>../../samples/data/ProcessingData</url>
<commonsCSVMetaData>
<xIndex>10</xIndex>
<yIndex>11</yIndex>
<separator>,</separator>
</commonsCSVMetaData>
</datastore>
</datastores>
</application>
GIS service dynamic encryption config
file
GIS Services Dynamic Encryption config file
iserver-svcworkkeymappings.xml, located at the config (【SuperMap iServer
installation directory】\webapps\iserver\WEB-INF\config) folder, which
can be used to prevent data crawling and improve the security of the server.
The configuration file stores the mapping relationship between the GIS
service to be encrypted, the encryption key, and the URL requests of the
service, that is, only one key can be used for one service type, and this
key is used for multiple URL requests under this service type. Refer to
"GIS Service
Dynamic Encryption Configuration" for the configuration method

